Warehousing services in India play a critical ...
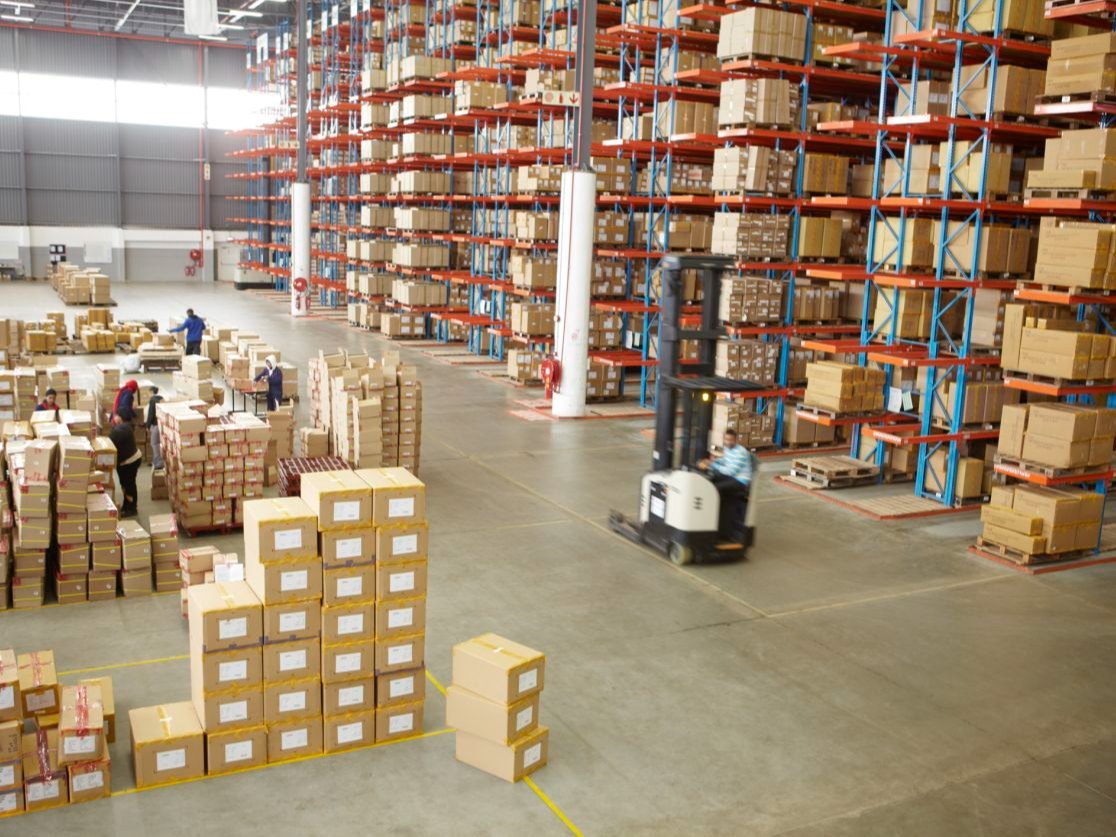

Warehousing services in India play a critical role in the country’s supply chain and logistics sector, especially given the rapid growth of e-commerce, retail, and manufacturing. Warehousing helps businesses manage inventory, reduce storage costs, and ensure timely delivery of products to customers. Here’s a breakdown of warehousing services in India: 1. Types of Warehousing Services Private Warehousing: Operated by businesses for their own use to store goods and inventory. It's typically used by large corporations that require dedicated space. Public Warehousing: Available for use by multiple clients, public warehouses are usually managed by third-party logistics (3PL) companies. Companies can rent space as needed, offering flexibility. Bonded Warehousing: Used for storing goods imported into India that are subject to customs duties. Goods can be stored in bonded warehouses until customs duties are paid. Distribution Centers: Focused on the rapid movement of goods from suppliers to end customers. These centers often include value-added services like packaging and labeling. Cold Storage Warehouses: Specially designed to store perishable goods (like fruits, vegetables, dairy, and pharmaceuticals) at controlled temperatures. Automated Warehousing: Uses technology like robots, conveyors, and AI-based systems to manage inventory and streamline the storage and retrieval processes. 2. Warehousing Services Providers in India Several logistics and supply chain companies provide warehousing services in India, ranging from small local operators to large multinational corporations. Some of the prominent providers include: DHL Supply Chain India: A global leader in logistics that provides a range of warehousing services, including transportation, inventory management, and value-added services. Blue Dart Express: Known for providing air and ground express services, Blue Dart also offers warehousing and distribution solutions. Mahindra Logistics: Provides integrated logistics solutions, including warehousing and distribution, catering to sectors such as automotive, retail, and consumer goods. Gati: A leading logistics provider that offers warehousing, freight forwarding, and last-mile delivery services. XpressBees: A popular e-commerce logistics company offering warehousing and fulfillment services to online retailers. Tata Strategic: Offers supply chain solutions, including warehousing, inventory management, and distribution services across various sectors. WOW Express: Specializes in logistics and warehousing services, especially for e-commerce businesses. 3. Technology in Warehousing Technology is increasingly being used to improve efficiency and reduce costs in warehousing. Some key technologies include: Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): Helps track inventory in real-time, optimize space, and streamline order fulfillment processes. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID): Used for better tracking of goods, reducing errors, and increasing efficiency. Automation and Robotics: Automated sorting, picking, and packaging processes can speed up operations and reduce labor costs. Internet of Things (IoT): Sensors in warehouses can monitor conditions like temperature and humidity, especially in sensitive areas like cold storage. Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-driven analytics help improve demand forecasting, inventory management, and warehouse layout optimization. 4. Warehousing Costs in India Warehousing costs in India depend on multiple factors: Location: Warehouses in major cities or industrial hubs tend to be more expensive. Logistics hubs such as Mumbai, Delhi, Chennai, and Bangalore have higher costs. Space Requirements: Larger warehouses generally cost more in terms of rent and operational expenses. Value-Added Services: Additional services like packaging, labeling, and inventory management can increase costs. Technology and Automation: The implementation of advanced technologies can lead to higher initial investment costs, though they may reduce long-term operational expenses. 5. Key Benefits of Warehousing in India Improved Inventory Management: Proper warehousing ensures businesses can maintain a balance between supply and demand, avoiding stockouts or overstocking. Faster Delivery: Strategic placement of warehouses across the country enables quicker distribution, particularly in last-mile delivery. Reduced Costs: Shared warehousing services reduce the financial burden of maintaining dedicated facilities for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Increased Efficiency: Modern warehousing facilities use automation and technology to streamline operations, saving time and reducing human error. Regulatory Compliance: Bonded and specialized warehouses help businesses comply with government regulations regarding taxes, tariffs, and product standards. 6. Challenges in the Indian Warehousing Sector Infrastructure Issues: Despite improvements, India’s logistics infrastructure, including roads and transportation networks, still faces challenges, especially in rural or remote areas. Regulatory Complexity: Different state policies, tax regimes (like GST), and compliance standards can create operational challenges for warehousing. Cost Inefficiency: High real estate prices in key areas and increasing labor costs may affect the overall cost-efficiency of warehousing operations. Skilled Labor Shortage: The demand for skilled workers in warehousing operations (such as warehouse managers and technology specialists) exceeds the available talent pool. 7. Future Trends in Warehousing in India E-commerce Growth: With the rapid expansion of online shopping, e-commerce-driven demand for warehousing services continues to rise. Sustainability: There’s a growing focus on green warehousing practices, such as using renewable energy sources and adopting sustainable packaging materials. Multi-Modal Transport Integration: The future of warehousing in India will see more integration between rail, road, and air transport, making supply chains more resilient. Urban Warehousing: As cities grow and e-commerce demand rises, urban warehouses are becoming increasingly important for last-mile delivery. AI and Data Analytics: AI-powered forecasting, predictive analytics, and machine learning will further optimize warehouse operations, improving efficiency and reducing costs. Conclusion India’s warehousing services are vital for the country’s logistics and supply chain management. With the rapid rise of e-commerce, automation, and advanced technologies, the warehousing sector is poised for continued growth. Businesses in India must evaluate the type of warehousing that best suits their needs—whether it’s private, public, or automated—and stay abreast of technological innovations to stay competitive.
Keywords
Subscribe for latest offers & updates
We hate spam too.